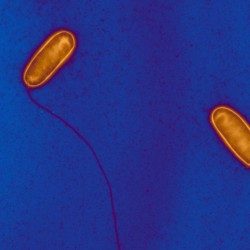
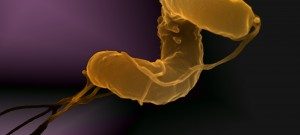
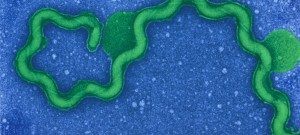
Besides their major role in many infectious diseases, bacteria also serve as models to understand fundamental biological mechanisms. The research performed in the Department of Microbiology mainly focuses on the molecular characterization of functions that enable bacteria to interact with their environment and, in some cases, to cause diseases.
The scientists of the Department of Microbiology study various bacteria and Archaea (and their viruses) as model systems to analyze fundamental biological processes at the population, cellular and molecular levels. They also focus on mechanisms rendering some of these microorganisms virulent and enabling them to evade the host immune system, or to develop resistance to antibiotics. For these studies, the scientists of the Department of Microbiology possess a wide range of expertise and use diverse integrative approaches to improve our understanding of the biology of these microorganisms. These studies also constitute a prerequisite for the development of new therapies or new diagnostic tools that can be used to treat or prevent bacterial infections. The Department of Microbiology includes 20 teams: 15 research teams, 1 Institut Pasteur/Paris University laboratory, and 4 collections. Three entities also host a National Reference Center and 2 are WHO Collaborating Centers. In addition, several research teams from other departments (Genomes & Genetics, Structural Biology and Chemistry and Infection & Epidemiology) are affiliated to the Department of Microbiology. The Department also hosts a joint research entity with the CNRS (French National Center for Scientific Research) – UMR2001.
_______________________
Click to access to the
______________________

Schiaffi V, Barras F and Bouveret E (2024) Matching the β-oxidation gene repertoire with the wide diversity of fatty acids. Curr Opin Microbiol Feb;77:102402.
Morel C, Lemerle E, Tsai FC, Obadia T, Srivastava N, Marechal M, Salles A, Albert M, Stefani C, Benito Y, Vandenesch F, Lamaze C, Vassilopoulos S, Piel M, Bassereau P, Gonzalez-Rodriguez D, Leduc C, Lemichez E (2024), Caveolin-1 protects endothelial cells from extensive expansion of transcellular tunnel by stiffening the plasma membrane, Elife. Mar 22;12:RP92078.
Maure A, Lawarée E, Fiorentino F, Pawlik A, Gona S, Giraud-Gatineau A, Eldridge MJG, Danckaert A, Hardy D, Frigui W, Keck C, Gutierrez C, Neyrolles O, Aulner N, Mai A, Hamon M, Barreiro LB, Brodin P, Brosch R, Rotili D, and Tailleux L. (2024) A host-directed oxadiazole compound potentiates antituberculosis treatment via zinc poisoning in human macrophages and in a mouse model of infection. PLoS Biol. Apr 29;22(4):e3002259.
Kevin Whelan, Aaron S Bancil, James O Lindsay, Benoit Chassaing (2024), Ultra-processed foods and food additives in gut health and disease, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol Jun;21(6):406-427. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38388570/
Zongo P D, Cabanel N, Royer G, Depardieu F, Hartmann A, Naas T, Glaser P, Rosinski-Chupin I, (2024), An antiplasmid system drives antibiotic resistance gene integration in carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli lineages. Nat Commun 15, 4093. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48219-y