Présentation
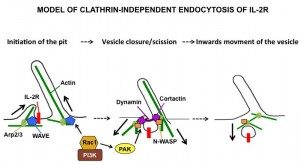
Endocytosis is an essential process used to internalize a wide range of molecules, and involved in many processes such as cell migration, cell division, immunity and pathogen invasion. Several endocytic pathways exist, enabling the entry of specific cargos. Clathrin-independent endocytosis (CIE) pathways are still not well understood. Cytokine receptors like interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R) were first physiological examples of cargos taken up by CIE. They are attractive cargos since they transduce the signal essential for the immune response. Cytokine receptor endocytosis tightly controls the proliferation signal. We have previously identified several factors involved in this CIE pathway, mainly proteins linked to actin and dynamin such as cortactin, N-WASP, the WAVE complex, Arp2/3, PI3K, Vav2, Rac1, and PAKs but also protein bending membranes like endophilin.
A unique feature of CIE is the absence of a coat protein that drives the pit formation, raising the question on how the CIE vesicle is initiated.
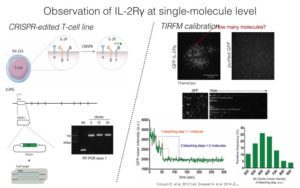
Protein clustering is known to mediate forces that can induce membrane conformational changes thus we want to understand the role of IL-2R clustering in its uptake. To determine IL-2Rγ stoichiometry we generated a CRISPR-edited T-cell line endogenously expressing GFP-IL-2Rγ, and analyzed at the plasma membrane by TIRF microscopy coupled to a single-molecule calibration and endocytic tracking method.
Our data identified three different populations of IL-2Rγ according to their lifetimes: a short-lived population, likely corresponding to newly secreted receptor; a long-lived population representing the actively endocytic receptor; and a static population. IL-2Rγ seems to be secreted to the plasma membrane as a pre-cluster of three molecules, which then undergoes addition of further receptor molecules creating an endocytic viable cluster of four to six molecules. The static population is characterized by a higher number of molecules, suggesting that larger complexes might render the receptor inefficient for endocytosis. The ligand, IL-2, leads to an increase in the proportion of endocytic viable clusters, in the number of IL-2Rγ molecules per cluster, and to a higher rate of receptor uptake, stressing the importance of clustering for CIE internalization.
Our next goal is to use super-resolution technique to confirm these data and the general stoechiometry of IL-2R at the plasma membrane by performing 3D Single Molecule Localization Microscope (SMLM) analysis on fixed samples.
- Characterize at the molecular level clathrin-independent endocytosis.
- Analyse the dynamics of several endocytic mechanisms.
- Link between cytokine receptor endocytosis,signalling and cell organization
- What are the factors initiating the CIE vesicle?
- How and when the endocytic factors are recruited?
Collaboration:
- Jean-Christophe Olivo-Marin’s group (IP): Thibault Lagache, Alexandre Dufour, Vannry Meas-Yedid. Computational imaging of clathrin-independent endocytosis dynamics
- Fernando Arenzana’ group (IP): Anne Brelot, Bernard Lagane, Fanny Momboisse. Heterogeneity of CC Chemokine Receptor 5 (CCR5) conformations and cluster of cytokine receptors by single molecule imaging analysis
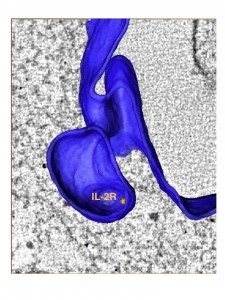
- Michael Trichet (UPMC Paris) and Eija Jokitalo (University of Helsinki, Finland). Ultrastructure of IL-2R pit
- Harvey McMahon (MRC cambridge) and Emmanuel Boucrot (UCL London). Role of endophilin in endocytosis.
- Alexis Gautreau (Ecole Polytechnique). Role of the WAVE complex in endocytosis
- Ali Amara (IUH, Paris) and Nolwen Jouvenet (IP)’s teams: Yellow fever viruses endocytosis
Techniques:
- Microscopy: Live spinning disc, Confocal, Total internal reflexion Fluorescent Microscopy (TIRF, movie1,2), Electron microscopy, Tomography (movies 3,4)
- Image analysis: Single molecules tracking, cluster organization, co-localization (ICY)
- Cell and molecular biology: siRNA, Gene editing, immunofluorescence, FACS
Ma video is about: