Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 31703112
PLoS Pathog. 2019 Nov;15(11):e1008069
Direct link to open access publication:
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1008069
Abstract
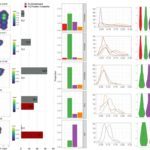
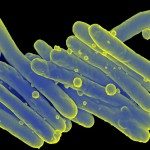
Free-living amoebae are thought to represent an environmental niche in which amoeba-resistant bacteria may evolve towards pathogenicity. To get more insights into factors playing a role for adaptation to intracellular life, we characterized the transcriptomic activities of the emerging pathogen Mycobacterium abscessus in amoeba and murine macrophages (Mϕ) and compared them with the intra-amoebal transcriptome of the closely related, but less pathogenic Mycobacterium chelonae. Data on up-regulated genes in amoeba point to proteins that allow M. abscessus to resist environmental stress and induce defense mechanisms, as well as showing a switch from carbohydrate carbon sources to fatty acid metabolism. For eleven of the most upregulated genes in amoeba and/or Mϕ, we generated individual gene knock-out M. abscessus mutant strains, from which ten were found to be attenuated in amoeba and/or Mϕ in subsequence virulence analyses. Moreover, transfer of two of these genes into the genome of M. chelonae increased the intra-Mϕ survival of the recombinant strain. One knock-out mutant that had the gene encoding Eis N-acetyl transferase protein (MAB_4532c) deleted, was particularly strongly attenuated in Mϕ. Taken together, M. abscessus intra-amoeba and intra-Mϕ transcriptomes revealed the capacity of M. abscessus to adapt to an intracellular lifestyle, with amoeba largely contributing to the enhancement of M. abscessus intra-Mϕ survival.