About
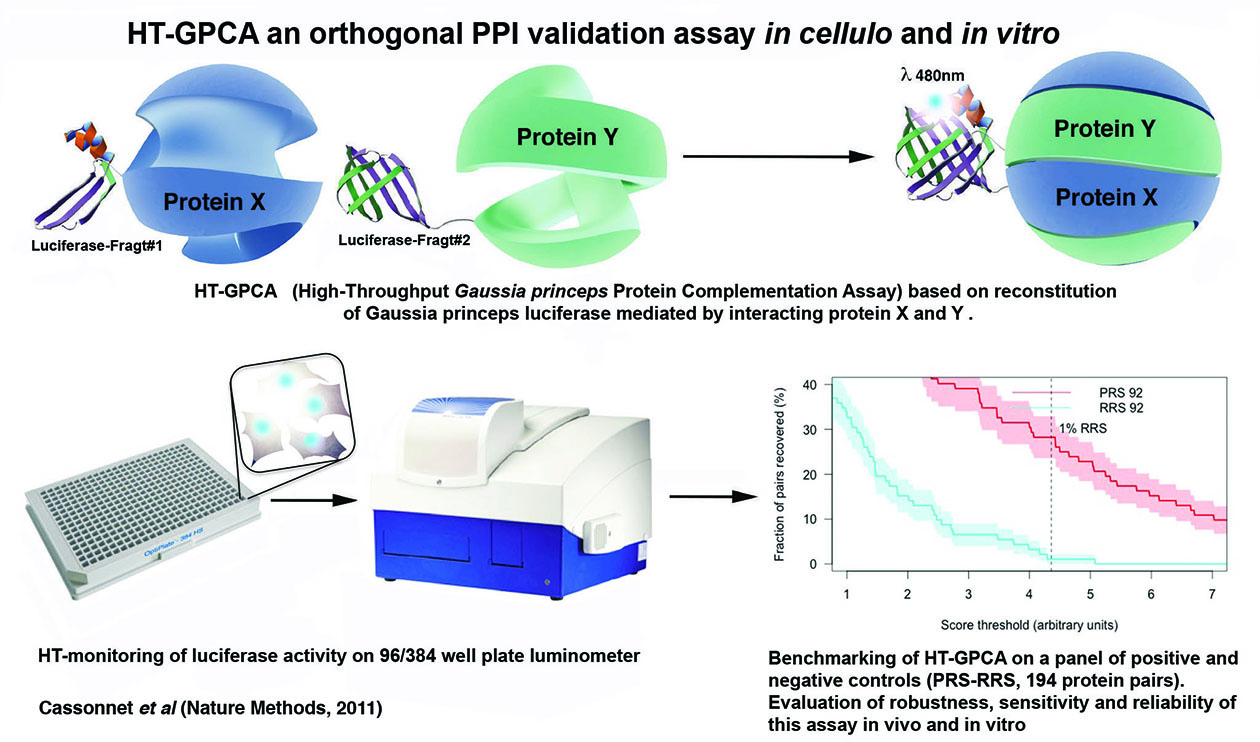
In order to increase the pipeline throughput this assay has been implemented in a 96-well plate format suitable for robotic automation of pipetting steps. Plate reading is performed on the last generation Berthold luminometer using a very sensitive, low-noise photomultiplier tube. Reading time as well as reagent consumption have been optimized in order to increase the flow rate and decrease costs. These developments especially in vitro GPCA should improve the assay’s integration on robotic platform as well as the readout flow (3h instead of 3 days) to achieve a high level of reliability and robustness.
GPCA references :
Cassonnet et al, Nature Methods. 2011
Muller et al, PLoS Pathog. 2012
Neveu et al, PLoS Pathog. 2012
Neveu et al, Methods. 2012
Bouraï et al, J Virol. 2012
Munier et al, Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013
Fournier et al, PLoS Pathog. 2014
Hill et al, Genes Dev. 2014
Sahni et al, Cell. 2015
Ramirez et al, Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015
Vincentelli et al, Nature Methods. 2015



