Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 28840795
Link to DOI – 10.1099/ijsem.0.002065
Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2017 Sep; 67(9): 3192-3197
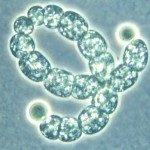
Six Gram-negative, non-motile, non-spore-forming, non-pigmented, oxidase- and catalase-positive bacterial strains were deposited in 1972, in the Collection of the Institut Pasteur (CIP), Paris, France. The strains, previously identified as members of the genus Moraxella on the basis of their phenotypic and biochemical characteristics, were placed within the genus Psychrobacter based on the results from comparative 16S rRNA gene sequence studies. Their closest phylogenetic relatives were Psychrobacter sanguinis CIP 110993T, Psychrobacter phenylpyruvicus CIP 82.27T and Psychrobacter lutiphocae CIP 110018T. The DNA G+C contents were between 42.1 and 42.7 mol%. The predominant fatty acids were C18 : 1ω9c, C16 : 0, C12 : 0 3-OH, and C18 : 0. Average nucleotide identity between the six strains and their closest phylogenetic relatives, as well as their phenotypic characteristics, supported the assignment of these strains to two novel species within the genus Psychrobacter. The proposed names for these strains are Psychrobacter pasteurii sp. nov., for which the type strain is A1019T (=CIP 110853T=CECT 9184T), and Psychrobacter piechaudii sp. nov., for which the type strain is 1232T (=CIP110854T=CECT 9185T).
[embeddoc url=”https://research.pasteur.fr/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/research_pasteur-psychrobacter-pasteurii-and-psychrobacter-piechaudii-sp-nov-two-novel-species-within-the-genus-psychrobacter-ijsem-2017.pdf” download=”all” viewer=”google”]