Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 35521527
Link to DOI – 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104233
iScience 2022 May; 25(5): 104233
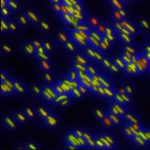
RNA turnover is a primary source of gene expression variation, in turn promoting cellular adaptation. Mycobacteria leverage reversible mRNA stabilization to endure hostile conditions. Although RNase E is essential for RNA turnover in several species, its role in mycobacterial single-cell physiology and functional phenotypic diversification remains unexplored. Here, by integrating live-single-cell and quantitative-mass-spectrometry approaches, we show that RNase E forms dynamic foci, which are associated with cellular homeostasis and fate, and we discover a versatile molecular interactome. We show a likely interaction between RNase E and the nucleoid-associated protein HupB, which is particularly pronounced during drug treatment and infection, where phenotypic diversity increases. Disruption of RNase E expression affects HupB levels, impairing Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth homeostasis during treatment, intracellular replication, and host spread. Our work lays the foundation for targeting the RNase E and its partner HupB, aiming to undermine M. tuberculosis cellular balance, diversification capacity, and persistence.