Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 25605428
Link to HAL – hal-01218596
Link to DOI – 10.1002/cyto.a.22629
Cytometry A 2015 Jun; 87(6): 568-79
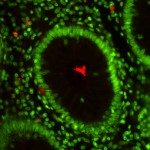
The quantitative analysis of molecule interactions in bioimaging is key for understanding the molecular orchestration of cellular processes and is generally achieved through the study of the spatial colocalization between the different populations of molecules. Colocalization methods are traditionally divided into pixel-based methods that measure global correlation coefficients from the overlap between pixel intensities in different color channels, and object-based methods that first segment molecule spots and then analyze their spatial distributions with second-order statistics. Here, we present a review of such colocalization methods and give a quantitative comparison of their relative merits in different types of biological applications and contexts. We show on synthetic and biological images that object-based methods are more robust statistically than pixel-based methods, and allow moreover to quantify accurately the number of colocalized molecules.