Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 40829804
Link to HAL – pasteur-05235945
Link to DOI – 10.1093/nar/gkaf786
Nucleic Acids Research, 2025, 53 (15), pp.gkaf786. ⟨10.1093/nar/gkaf786⟩
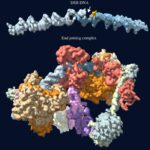
Repairing programmed DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) is crucial in the lifecycle of Paramecium tetraurelia, especially during its sexual reproduction phase when its somatic polyploid macronucleus is lost. The formation of a new macronucleus involves programmed genome rearrangements, introducing DNA DSBs at ∼45 000 loci. Paramecium tetraurelia employs a non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) mechanism for the faithful repair of these DSBs. There are four genes encoding DNA polymerases of family X in the genome, one of which was found recently to colocalize with other NHEJ proteins in the nucleus. Here we have characterized all four enzymes and shown that they are generally very faithful. They fall into two functional classes that may specialize in the distinct repair contexts encountered during DSB DNA repair. Biochemical assays, site-directed mutagenesis, and X-ray structures of mutants of human Polλ incorporating sequence determinants from P. tetraurelia PolX or metazoan Polβ are used to investigate the origin of their fidelity. Our findings suggest that Paramecium PolX enzymes may represent evolutionary intermediates between metazoan Polβ and Polλ. A general classification of DNA PolXs based on clustering methods indicates that our results can be generalized to plant DNA PolXs (Polλ-like) involved in DSB DNA repair generated by CRISPR–Cas9 engineering.