Présentation
Mucosal homeostasis requires a delicate equilibrium between immune mechanisms and commensal microorganisms that impacts on the development and maintenance of critical physiological processes including digestion, metabolism or host defense. Several infectious or inflammatory disorders have been associated with dysregulated intestinal homeostasis. The immune system, and notably the innate compartment, plays an essential role in the regulation of host-microbe interactions, but several aspects of this immunological relationship remain unclear.
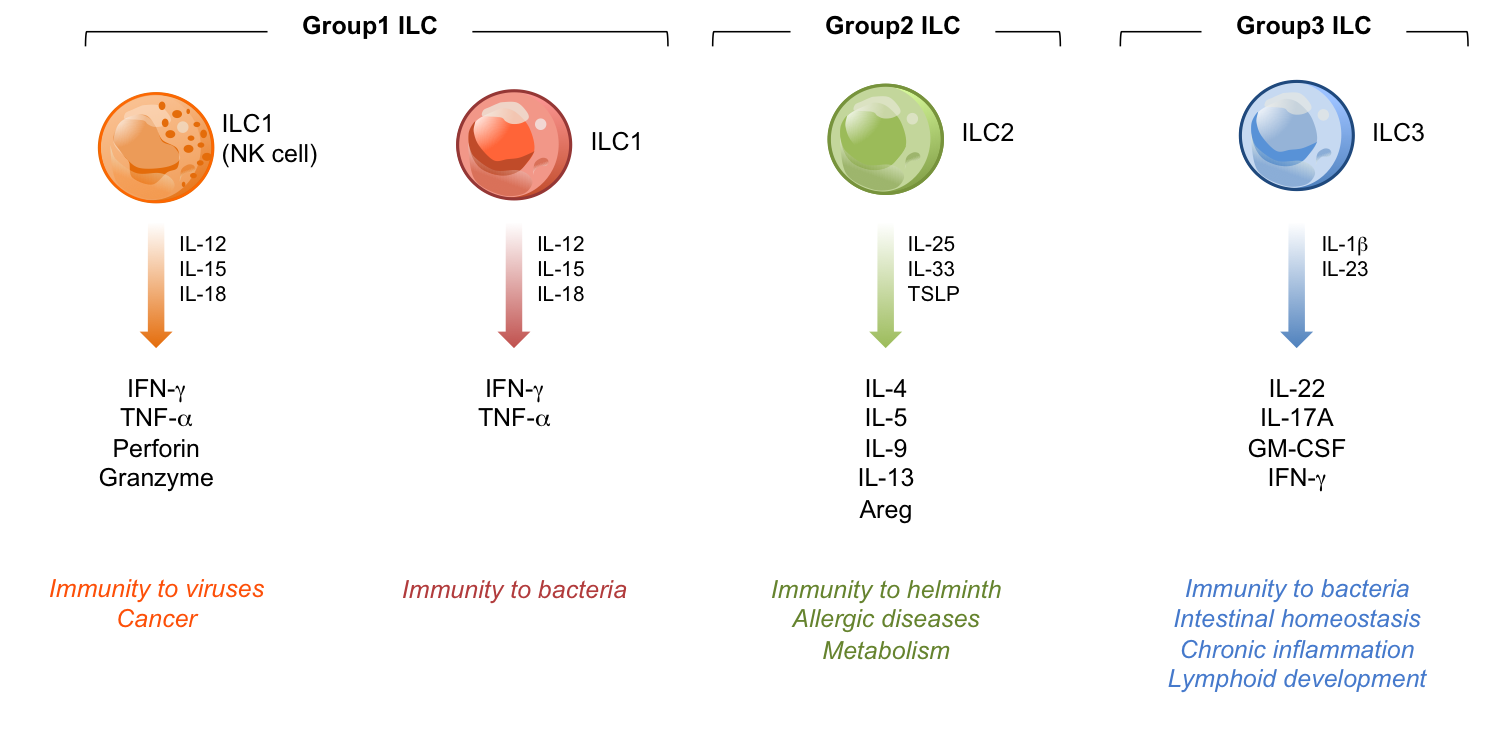
Recently, additional innate lymphocytes have been discovered named innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) in both humans and mice (1-8). ILCs are early effectors of immunity and provide a means to rapidly respond to infection or inflammation, and are distinguished from T and B cells of the adaptive immune response. Three groups of ILCs are now described: ILC1, ILC2 and ILC3. ILC1 consists of NK cells and other interferon-g producing innate lymphocytes characterized by expression of the transcription factors T-bet and/Eomes. ILC2 secrete ‘TH2-like’ cytokines under the control of the transcription factors GATA-3 and RORa. ILC3 includes several phenotypically distinct cells that express and require the transcription factor RORgt in order to produce notably the cytokines IL-17 and IL-22.
The ILC subsets have been implicated in a wide range of physiological processes including tissue homeostasis and repair, immune defense or development of lymphoid organs. We study ILCs development from hematopoietic precursors using mouse models. Our goal is to understand how ILCs differentiate and function in the context of infection and inflammation. (9-18). These mouse based studies are fundamental in nature, but may provide new insights into the ILC biology that could be applicable to human disease states.
References
1: Serafini N, Vosshenrich CA, Di Santo JP. Transcriptional regulation of innate lymphoid cell fate. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015
2: Eberl G, Colonna M, Di Santo JP, McKenzie AN. Innate lymphoid cells. Innate lymphoid cells: a new paradigm in immunology. Science. 2015
3: Eberl G, Di Santo JP, Vivier E. The brave new world of innate lymphoid cells. Nat Immunol. 2015
4: Di Santo JP. Staying innate: transcription factor maintenance of innate lymphoid cell identity. Immunol Rev. 2014
5: Tindemans I, Serafini N, Di Santo JP, Hendriks RW. GATA-3 function in innate and adaptive immunity. Immunity. 2014
6: Spits H, Artis D, Colonna M, Diefenbach A, Di Santo JP, Eberl G, Koyasu S, Locksley RM, McKenzie AN, Mebius RE, Powrie F, Vivier E. Innate lymphoid cells–a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014
7: Xu W, Di Santo JP. Taming the beast within: regulation of innate lymphoid cell homeostasis and function. J Immunol. 2013
8: Spits H, Di Santo JP. The expanding family of innate lymphoid cells: regulators and effectors of immunity and tissue remodeling. Nat Immunol. 2011
9: Xu W, et al. NFIL3 orchestrates the emergence of common helper innate lymphoid cell precursors. Cell Rep. 2015
10: Satoh-Takayama N, et al. . The chemokine receptor CXCR6 controls the functional topography of interleukin-22 producing intestinal innate lymphoid cells. Immunity. 2014
11: Merzoug LB, et al. Conditional ablation of NKp46+ cells using novel Ncr1(greenCre) mouse strain: NK cells are essential for protection against pulmonary B16 metastases. Eur J Immunol. 2014
12: Serafini N, et al. Gata3 drives development of RORγt+ group 3 innate lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 2014
13: Klein Wolterink RG, et al. Essential dose-dependent role for the transcription factor Gata3 in the development of IL-5+ and IL-13+ type 2 innate lymphoid cells. PNAS. 2013
14: Satoh-Takayama N, et al. Lymphotoxin-β receptor-independent development of intestinal IL-22-producing NKp46+ innate lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 2011
15: Satoh-Takayama N, et al. IL-7 and IL-15 independently program the differentiation of intestinal CD3-NKp46+ cell subsets from Id2-dependent precursors. J Exp Med. 2010
16: Satoh-Takayama N, et al. The natural cytotoxicity receptor NKp46 is dispensable for IL-22-mediated innate intestinal immune defense against Citrobacter rodentium. J Immunol. 2009
17: Satoh-Takayama N, et al. Microbial flora drives interleukin 22 production in intestinal NKp46+ cells that provide innate mucosal immune defense. Immunity. 2008
18: Vosshenrich CA, et al. A thymic pathway of mouse natural killer cell development characterized by expression of GATA-3 and CD127. Nat Immunol. 2006