Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 24982306
J. Bacteriol. 2014 Sep;196(18):3234-48
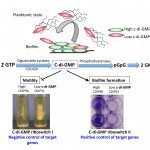
Clostridium difficile is an emergent human pathogen and the most common cause of nosocomial diarrhea. Our recent data strongly suggest the importance of RNA-based mechanisms for the control of gene expression in C. difficile. In an effort to understand the function of the RNA chaperone protein Hfq, we constructed and characterized an Hfq-depleted strain in C. difficile. Hfq depletion led to a growth defect, morphological changes, an increased sensitivity to stresses, and a better ability to sporulate and to form biofilms. The transcriptome analysis revealed pleiotropic effects of Hfq depletion on gene expression in C. difficile, including genes encoding proteins involved in sporulation, stress response, metabolic pathways, cell wall-associated proteins, transporters, and transcriptional regulators and genes of unknown function. Remarkably, a great number of genes of the regulon dependent on sporulation-specific sigma factor, SigK, were upregulated in the Hfq-depleted strain. The altered accumulation of several sRNAs and interaction of Hfq with selected sRNAs suggest potential involvement of Hfq in these regulatory RNA functions. Altogether, these results suggest the pleiotropic role of Hfq protein in C. difficile physiology, including processes important for the C. difficile infection cycle, and expand our knowledge of Hfq-dependent regulation in Gram-positive bacteria.