Link to HAL – Click here
Link to DOI – 10.1093/ve/veab055
Virus Evolution, 2021, veab055
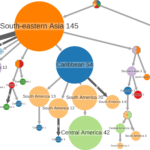
Understanding of pandemics depends on the characterization of pathogen collections from well-defined and demographically diverse cohorts. Since its emergence in Congo almost a century ago, Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) has geographically spread and genetically diversified into distinct viral subtypes. Phylogenetic analysis can be used to reconstruct the ancestry of the virus to better understand the origin and distribution of subtypes. We sequenced two 3.6-kb amplicons of HIV-1 genomes from 3,197 participants in a clinical trial with consistent and uniform sampling at sites across 35 countries and analyzed our data with another 2,632 genomes that comprehensively reflect the HIV-1 genetic diversity. We used maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis coupled with geographical information to infer the state of ancestors. The majority of our sequenced genomes (n = 2,501) were either pure subtypes (A–D, F, and G) or CRF01_AE. The diversity and distribution of subtypes across geographical regions differed; USA showed the most homogenous subtype population, whereas African samples were most diverse. We delineated transmission of the four most prevalent subtypes in our dataset (A, B, C, and CRF01_AE), and our results suggest both continuous and frequent transmission of HIV-1 over country borders, as well as single transmission events being the seed of endemic population expansions. Overall, we show that coupling of genetic and geographical information of HIV-1 can be used to understand the origin and spread of pandemic pathogens.