Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 20844221
J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010 Nov;48(11):4028-34
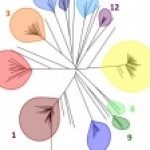
Candida glabrata has emerged as the second most common etiologic agent, after Candida albicans, of superficial and invasive candidiasis in adults. Strain typing is essential for epidemiological investigation, but easy-to-use and reliable typing methods are still lacking. We report the use of a multilocus microsatellite typing method with a set of eight markers on a panel of 180 strains, including 136 blood isolates from hospitalized patients and 34 digestive tract isolates from nonhospitalized patients. A total of 44 different alleles were observed, generating 87 distinct genotypes. In addition to perfect reproducibility, typing ability, and stability, the method had a discriminatory power calculated at 0.97 when all 8 markers were associated, making it suitable for tracing strains. In addition, it is shown that digestive tract isolates differed from blood culture isolates by exhibiting a higher genotypic diversity associated with different allelic frequencies and preferentially did not group in clonal complexes (CCs). The demonstration of the occurrence of microevolution in digestive strains supports the idea that C. glabrata can be a persistent commensal of the human gut.