Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 18162469
J Biol Chem 2008 Feb; 283(9): 5960-70
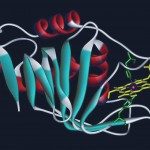
Heme carrier HasA has a unique type of histidine/tyrosine heme iron ligation in which the iron ion is in a thermally driven two spin states equilibrium. We recently suggested that the H-bonding between Tyr75 and the invariantly conserved residue His83 modulates the strength of the iron-Tyr75 bond. To unravel the role of His83, we characterize the iron ligation and the electronic properties of both wild type and H83A mutant by a variety of spectroscopic techniques. Although His83 in wild type modulates the strength of the Tyr-iron bond, its removal causes detachment of the tyrosine ligand, thus giving rise to a series of pH-dependent equilibria among species with different axial ligation. The five coordinated species detected at physiological pH may represent a possible intermediate of the heme transfer mechanism to the receptor.