Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 22608967
Link to DOI – 10.1016/j.str.2012.03.024
Structure 2012 Jun; 20(6): 1107-17
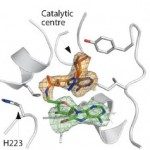
Making new ligands for a given protein by in situ ligation of building blocks (or fragments) is an attractive method. However, it suffers from inherent limitations, such as the limited number of available chemical reactions and the low information content of usual chemical library deconvolution. Here, we describe a focused screening of adenosine derivatives using X-ray crystallography. We discovered an unexpected and biocompatible chemical reactivity and have simultaneously identified the mode of binding of the resulting products. We observed that the NAD kinase from Listeria monocytogenes (LmNADK1) can promote amide formation between 5′-amino-5′-deoxyadenosine and carboxylic acid groups. This unexpected reactivity allowed us to bridge in situ two adenosine derivatives to fully occupy the active NAD site. This guided the design of a close analog showing micromolar inhibition of two human pathogenic NAD kinases and potent bactericidal activity against Staphylococcus aureus in vitro.