Lien vers Pubmed [PMID] – 25254624
Curr Opin Pharmacol 2014 Oct;18:61-8
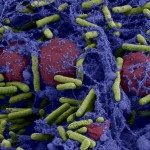
Biofilms formed by pathogenic bacteria and fungi are associated with a wide range of diseases, from device-related infections (such as catheters or prosthetic joints) to chronic infections occurring on native tissues (such as lung infections in cystic fibrosis patients). Biofilms are therefore responsible for an important medical and economic burden. Currently used antibiotics have mostly been developed to target exponentially growing microorganisms and are poorly effective against biofilms. In particular, even high concentrations of bactericidal antibiotics are inactive against a subset of persistent biofilm bacteria, which can cause infection recurrence despite prolonged treatments. While the search for a magic bullet antibiotic effective against both planktonic and biofilm bacteria is still active, alternative preventive and curative approaches are currently being developed either limiting adhesion or biofilm formation or targeting biofilm tolerance by killing persister bacteria. Most of these approaches are adjunctive using new molecules in combination with antibiotics. This review presents promising approaches or strategies that could improve our ability to prevent or eradicate bacterial biofilms in medical settings.