Lien vers Pubmed [PMID] – 31031012
Am J Hum Genet. 2019 May 2;104(5):815-834
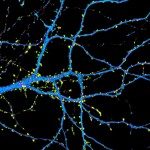
We identified individuals with variations in ACTL6B, a component of the chromatin remodeling machinery including the BAF complex. Ten individuals harbored bi-allelic mutations and presented with global developmental delay, epileptic encephalopathy, and spasticity, and ten individuals with de novo heterozygous mutations displayed intellectual disability, ambulation deficits, severe language impairment, hypotonia, Rett-like stereotypies, and minor facial dysmorphisms (wide mouth, diastema, bulbous nose). Nine of these ten unrelated individuals had the identical de novo c.1027G>A (p.Gly343Arg) mutation. Human-derived neurons were generated that recaptured ACTL6B expression patterns in development from progenitor cell to post-mitotic neuron, validating the use of this model. Engineered knock-out of ACTL6B in wild-type human neurons resulted in profound deficits in dendrite development, a result recapitulated in two individuals with different bi-allelic mutations, and reversed on clonal genetic repair or exogenous expression of ACTL6B. Whole-transcriptome analyses and whole-genomic profiling of the BAF complex in wild-type and bi-allelic mutant ACTL6B neural progenitor cells and neurons revealed increased genomic binding of the BAF complex in ACTL6B mutants, with corresponding transcriptional changes in several genes including TPPP and FSCN1, suggesting that altered regulation of some cytoskeletal genes contribute to altered dendrite development. Assessment of bi-alleic and heterozygous ACTL6B mutations on an ACTL6B knock-out human background demonstrated that bi-allelic mutations mimic engineered deletion deficits while heterozygous mutations do not, suggesting that the former are loss of function and the latter are gain of function. These results reveal a role for ACTL6B in neurodevelopment and implicate another component of chromatin remodeling machinery in brain disease.