Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 22090096
J. Virol. 2012 Jan;86(2):909-18
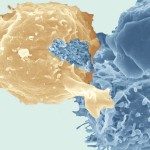
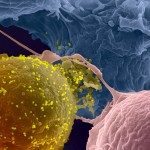
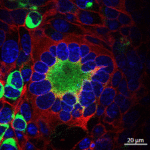
Foamy viruses (FV) are nonpathogenic retroviruses that have cospeciated with primates for millions of years. FV can be transmitted through severe bites from monkeys to humans. Viral loads remain generally low in infected humans, and no secondary transmission has been reported. Very little is known about the ability of FV to trigger an innate immune response in human cells. A few previous reports suggested that FV do not induce type I interferon (IFN) in nonhematopoietic cells. Here, we examined how human hematopoietic cells sense FV particles and FV-infected cells. We show that peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), and the pDC-like cell line Gen2.2 detect FV, produce high levels of type I IFN, and express the IFN-stimulated gene MxA. Fewer than 20 FV-infected cells are sufficient to trigger an IFN response. Both prototypic and primary viruses stimulated IFN release. Donor cells expressing a replication-defective virus, carrying a mutated reverse transcriptase, induced IFN production by target cells as potently as wild-type virus. In contrast, an FV strain with env deleted, which does not produce viral particles, was inactive. IFN production was blocked by an inhibitor of endosomal acidification (bafilomycin A1) and by an endosomal Toll-like receptor (TLR) antagonist (A151). Silencing experiments in Gen2.2 further demonstrated that TLR7 is involved in FV recognition. Therefore, FV are potent inducers of type I IFN by pDCs and by PBMCs. This previously underestimated activation of the innate immune response may be involved in the control of viral replication in humans.