Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 22127214
Nat. Methods 2011 Dec;8(12):990-2
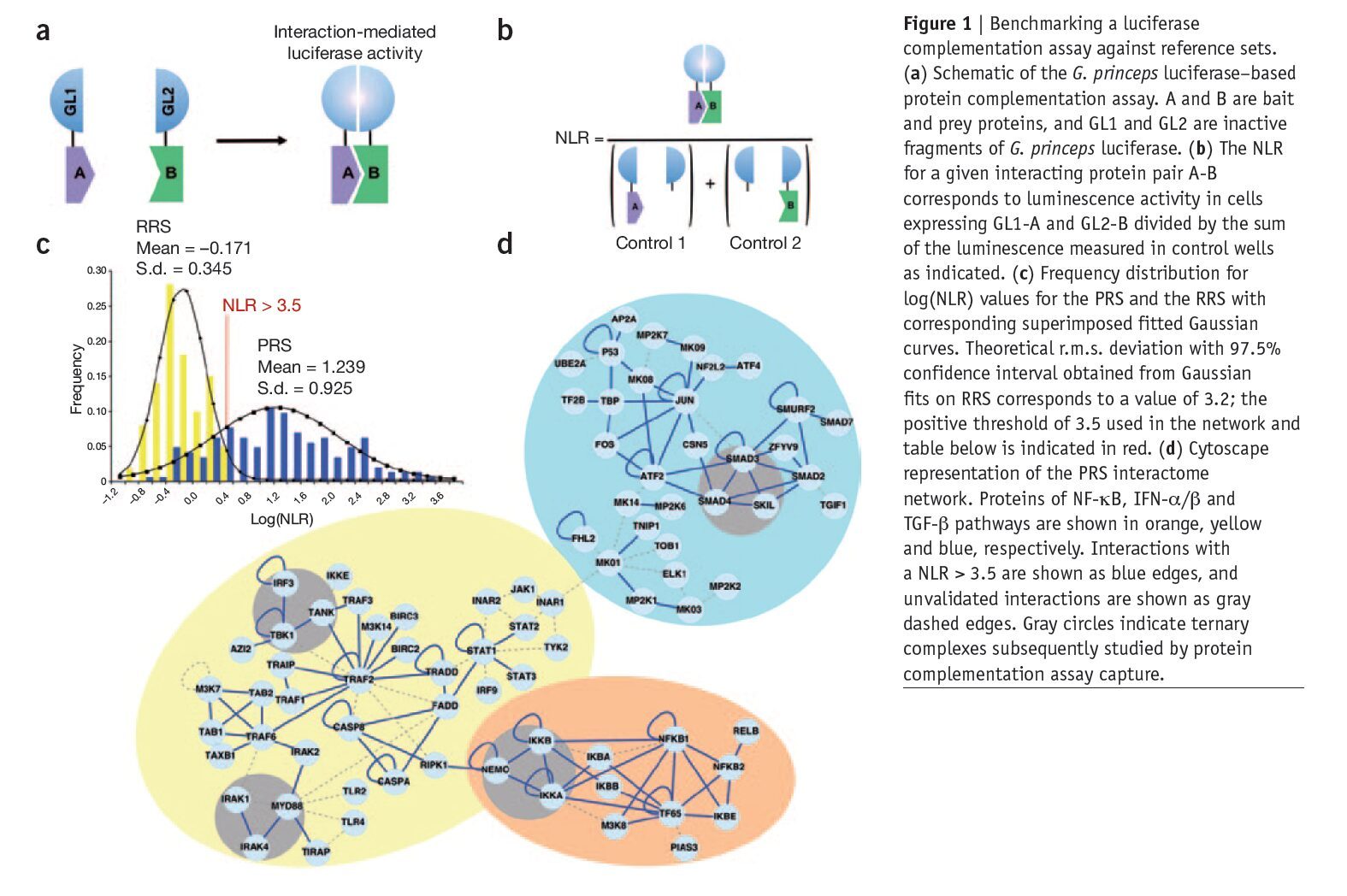
Mapping protein-protein interactions (PPIs) has proven instrumental in functional proteomics. Large PPI databases have been established by literature mining or using high-throughput screening methods; this information requires cross-validation to increase coverage and accuracy. Previously published papers have argued for the use of defined reference sets for the benchmarking of screening methods for PPIs. Here we describe a high-throughput system for orthogonal validation of PPI datasets, and we benchmark its performance against newly curated and previously reported reference sets. Based on a previously reported PPI-detection assay relying on complementation of split Gaussia princeps luciferase, we engineered two mammalian expression vectors for high-throughput PPI detection. In this assay, we monitored PPIs by measuring interaction-mediated normalized luminescence ratio (NLR). We benchmarked the accuracy and sensitivity of this system using an a priori ‘negative’ or non-interacting set of 100 random human protein pairs (the random reference set, RRS) and a positive or interacting set composed of 143 PPIs from NF-kB, IFN-a/b and TGF-b pathways supported in the literature by at least three different experimental methods4 (the positive reference set, PRS).