About
Epithelia form sheets of interconnected cells that are polarized along an apical-basal axis and perform selective exchange and barrier functions. Epithelia are dynamic structures that undergo remodeling associated with cell shape changes and neighbor exchange. The fly embryo provides an outstanding model system to study how epithelia form and change shape during morphogenesis. The developmental programs that regulate morphogenetic changes have been best studied in fly epithelia. In recent work, we have discovered that the conserved E3 ubiquitin ligase Neuralized (which is best known for its role in Notch signaling) regulate epithelial morphogenesis in various developmental settings, including gastrulation and trans-epithelial migration.
Using a candidate gene approach, we identified Stardust (Sdt), a core Crumbs complex protein (6), as a direct target of Neur. Neur interacts with and down-regulates specific Sdt isoforms which include a Neur Binding Motif (NBM). Analysis of a CRISPR-induced deletion of these NBM-encoding isoforms showed that Neur acts via Sdt to down-regulate Crumbs and disrupt epithelium integrity. Results from a cell-based endocytosis assay indicates that Neur regulates the endocytosis of Crumbs via Sdt. While mutant analysis indicates that the regulation of Crumbs by Neur is not essential, Neur contributes to epithelium remodeling in specific developmental contexts. Thus, we uncovered a novel regulatory mechanism for the developmental control of Crumbs-mediated morphogenesis.
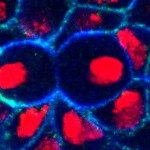
Figure (right): cross section view of a gastrulating embryo showing ventral cells (bottom) undergoing apical constriction, forming a ventral furrow (red: myosin; blue: nuclei; green: cell-cell junctions)
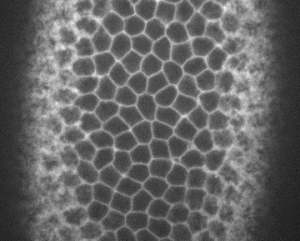
Movie (left): top view showing ventral cells undergoing apical constriction and invagination (live imaging of an embryo expressing a GFP-tagged membrane marker)
Using an innovative approach to deplete the maternal pool of Neur proteins, we studied the role of Neur in early embryos and showed that Neur regulates collective apical constriction and furrow formation in ventral cells. Also, reduced medio-apical Myosin (MyoII) levels were measured in ventral cells upon inhibition of Neur. Simulations of a 2D multiscale viscous model indeed predicted lowered apical forces in neur mutant embryos (collaboration with V. Conte, Barcelona). Conversely, loss of Brd led to increased medial MyoII in the ectoderm. Increased contractility in lateral cells explains why the ventral furrow initially forms but then unfolds in Brd mutant embryos. Indeed, decreasing contractility in the ectoderm, using a MyoII phosphatase, was sufficient to restore furrow invagination in Brd mutant embryos and, conversely, increasing contractility in the ectoderm mimicked the Brd mutant phenotype. Thus, the inhibition of Neur by Brd in the ectoderm differentiates the mechanics of the ectoderm from that of the mesoderm and patterns the activity of MyoII along the dorsal-ventral axis.
In summary, we have discovered two new functions of Neur, in junction remodeling via Sdt-Crumbs and in actomyosin contractility via an unknown target. In the embryo, Brd and Neur act downstream of dorsal-ventral patterning to establish a biomechanical difference between the mesoderm and the ectoderm. This is the first evidence that regulation of the mechanical properties of the ectoderm is critical for invagination of the mesoderm.
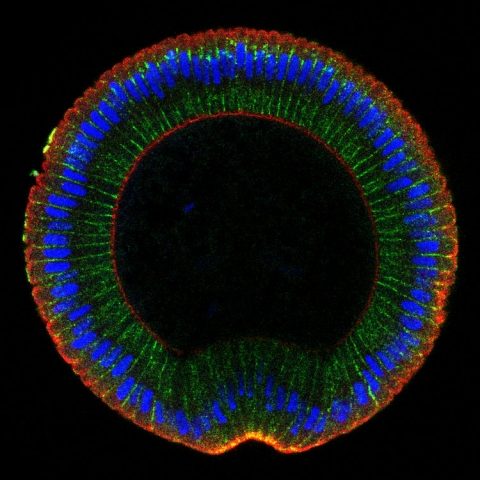
We are currently examining the role of Neur in coordinating cell fate with epithelial remodeling at the tissue scale at a differentiation front sweeping through the optic lobe neuroepithelium.
S. Chanet and F. Schweisguth (2012) Regulation of epithelial polarity by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Neuralized and the Bearded inhibitors in Drosophila. Nature Cell Biology, 14, 467-76
G. Perez-Mockus, K. Mazouni, V. Roca, G. Corradi, V. Conte and F. Schweisguth (2017) Spatial regulation of contractility by Neuralized and Bearded during furrow invagination in Drosophila. Nature Communications, 8, 1594
G. Perez-Mockus, V. Roca, K. Mazouni and F. Schweisguth (2017) Neuralized regulates Crumbs endocytosis and epithelium morphogenesis via specific Stardust isoforms. The Journal of Cell Biology, 205, 1405-20