About
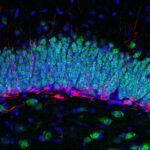
How does the brain distinguish between memories that closely resemble each other? The hippocampal dentate gyrus has been suggested to serve this purpose by generating non-overlapping memory representations in a process termed “pattern separation”. Intriguingly, during adult life, the dentate gyrus is constantly supplied with new neurons, providing new circuit elements that can incorporate into the neuronal network. How the activity of new adult-born neurons and mature granule cells combines to drive the production and storage of distinct memories represents a new frontier in understanding brain function. However, to determine how these neurons transform similar synaptic input patterns into decorrelated spike output patterns representing distinct memories, we need to monitor and manipulate their subthreshold and suprathreshold activity during behaviour. To address these challenges, we will combine molecular, physiological and optical approaches in the mouse dentate gyrus during navigation in a virtual reality environment. We will use intracellular recordings to assess how hippocampal neurons convert synaptic inputs into spike output, 2-photon Ca2+ imaging to monitor population activity in the hippocampal circuit, and optogenetic tools to causally test the involvement of specific cell types. These experiments will allow us to address the following key questions: 1. Which behaviours trigger action potentials in identified newborn and mature dentate gyrus neurons? 2. How do synaptic inputs drive spiking in newborn and mature neurons during behaviour? 3. How are small changes in an environment encoded by synaptic inputs to newborn and mature neurons? 4. Can we differentially manipulate the activity of new and mature cells to selectively interfere with animal behaviour during pattern separation and completion tasks? Understanding the role of new and mature neurons in hippocampal function will provide fundamental insights into the cellular mechanisms of memory formation.