Lien vers Pubmed [PMID] – 28336667
Science 2017 Mar;355(6331):1302-1306
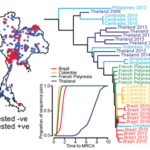
A fundamental mystery for dengue and other infectious pathogens is how observed patterns of cases relate to actual chains of individual transmission events. These pathways are intimately tied to the mechanisms by which strains interact and compete across spatial scales. Phylogeographic methods have been used to characterize pathogen dispersal at global and regional scales but have yielded few insights into the local spatiotemporal structure of endemic transmission. Using geolocated genotype (800 cases) and serotype (17,291 cases) data, we show that in Bangkok, Thailand, 60% of dengue cases living <200 meters apart come from the same transmission chain, as opposed to 3% of cases separated by 1 to 5 kilometers. At distances <200 meters from a case (encompassing an average of 1300 people in Bangkok), the effective number of chains is 1.7. This number rises by a factor of 7 for each 10-fold increase in the population of the "enclosed" region. This trend is observed regardless of whether population density or area increases, though increases in density over 7000 people per square kilometer do not lead to additional chains. Within Thailand these chains quickly mix, and by the next dengue season viral lineages are no longer highly spatially structured within the country. In contrast, viral flow to neighboring countries is limited. These findings are consistent with local, density-dependent transmission and implicate densely populated communities as key sources of viral diversity, with home location the focal point of transmission. These findings have important implications for targeted vector control and active surveillance.