Out of the results of the sole large-scale screening for inhibitors of SARS-CoV-1 main protease reported in 2013, attempts to improve the identified 3-pyridyl-bearing hits have been conducted in research laboratories, either on this enzyme or more recently on the closely related SARS-CoV-2 main protease. From the resulting structural information reported, we sought to design analogues featuring some of the components providing an affinity for the active site of these proteases along with a different scaffold, which would allow for further structure-activity relationship studies and/or pharmacological improvements. We describe here the introduction of a bridging component with the aim of stabilizing the ligand conformation adopted when bound to these proteases. Accordingly, this led us to prepare 3,3-disubstituted piperazin-2-ones from an array of ketones, via either a Bargellini reaction or a multistage condensation/cyclization/hydrolysis involving ethylene diamine and potassium cyanide. However, even the most elaborate and lipophilic biphenyl-bearing analogues displayed only a weak effect in a bioluminescence-based SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibition assay. https://www.thieme-connect.de/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/a-2519-9876
© Biologie structurale et chimie
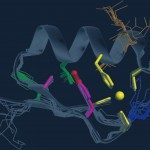
Structure du domaine en doigt de zinc de la protéine NEMO, déterminée par Résonance magnétique nucléaire (RMN).
Cette protéine jouant un rôle dans des maladies (cancer, inflammation), les connaissances acquises sur sa structure offrent de précieuses informations sur sa fonction.
Publication : Synthesis