Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 26014801
J. Infect. Dis. 2015 Nov;212(10):1646-55
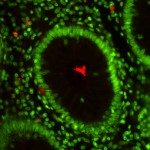
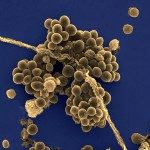
Streptococcus gallolyticus is an increasing cause of bacteremia and infective endocarditis in the elderly. Several epidemiological studies have associated the presence of this bacterium with colorectal cancer. We have studied the interaction of S. gallolyticus with human colonic cells. S. gallolyticus strain UCN34, adhered better to mucus-producing cells such as HT-29-MTX than to the parental HT-29 cells. Attachment to colonic mucus is dependent on the pil3 pilus operon, which is heterogeneously expressed in the wild-type UCN34 population. We constructed a pil3 deletion mutant in a Pil3 overexpressing variant (Pil3+) and were able to demonstrate the role of Pil3 pilus in binding to colonic mucus. Importantly, we showed that pil3 deletion mutant was unable to colonize mice colon as compared to the isogenic Pil3+ variant. Our findings establish for the first time a murine model of intestinal colonization by S. gallolyticus.