Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 24911516
PLoS ONE 2014;9(6):e99197
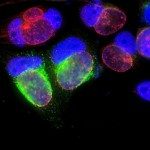
Chlamydiae are obligate intracellular bacteria. These pathogens develop inside host cells through a biphasic cycle alternating between two morphologically distinct forms, the infectious elementary body and the replicative reticulate body. Recently, C. trachomatis strains stably expressing fluorescent proteins were obtained. The fluorochromes are expressed during the intracellular growth of the microbe, allowing bacterial visualization by fluorescence microscopy. Whether they are also present in the infectious form, the elementary body, to a detectable level has not been studied. Here, we show that a C. trachomatis strain transformed with a plasmid expressing the green fluorescent protein (GFP) accumulates sufficient quantities of the probe in elementary bodies for detection by microscopy and flow cytometry. Adhesion of single bacteria was detected. The precise kinetics of bacterial entry were determined by microscopy using automated procedures. We show that during the intracellular replication phase, GFP is a convenient read-out for bacterial growth with several advantages over current methods. In particular, infection rates within a non-homogenous cell population are easily quantified. Finally, in spite of their small size, individual elementary bodies are detected by flow cytometers, allowing for direct enumeration of a bacterial preparation. In conclusion, GFP-expressing chlamydiae are suitable to monitor, in a quantitative manner, progression throughout the developmental cycle. This will facilitate the identification of the developmental steps targeted by anti-chlamydial drugs or host factors.