Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 15892870
Genome Biol. 2005;6(5):R42
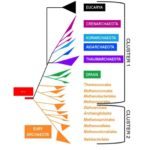
BACKGROUND: Cultivable archaeal species are assigned to two phyla — the Crenarchaeota and the Euryarchaeota — by a number of important genetic differences, and this ancient split is strongly supported by phylogenetic analysis. The recently described hyperthermophile Nanoarchaeum equitans, harboring the smallest cellular genome ever sequenced (480 kb), has been suggested as the representative of a new phylum — the Nanoarchaeota — that would have diverged before the Crenarchaeota/Euryarchaeota split. Confirming the phylogenetic position of N. equitans is thus crucial for deciphering the history of the archaeal domain.
RESULTS: We tested the placement of N. equitans in the archaeal phylogeny using a large dataset of concatenated ribosomal proteins from 25 archaeal genomes. We indicate that the placement of N. equitans in archaeal phylogenies on the basis of ribosomal protein concatenation may be strongly biased by the coupled effect of its above-average evolutionary rate and lateral gene transfers. Indeed, we show that different subsets of ribosomal proteins harbor a conflicting phylogenetic signal for the placement of N. equitans. A BLASTP-based survey of the phylogenetic pattern of all open reading frames (ORFs) in the genome of N. equitans revealed a surprisingly high fraction of close hits with Euryarchaeota, notably Thermococcales. Strikingly, a specific affinity of N. equitans and Thermococcales was strongly supported by phylogenies based on a subset of ribosomal proteins, and on a number of unrelated molecular markers.
CONCLUSION: We suggest that N. equitans may more probably be the representative of a fast-evolving euryarchaeal lineage (possibly related to Thermococcales) than the representative of a novel and early diverging archaeal phylum.