Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 17240531
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007 Apr;1770(4):495-505
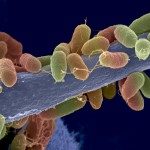
The homogeneous low molecular weight chitosans (LMWC) of molecular weight 9.5-8.5 kDa, obtained by pronase catalyzed non-specific depolymerization (at pH 3.5, 37 degrees C) of chitosan showed lyses of Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli more efficiently (100%) than native chitosan (<50%). IR and (1)H-NMR data showed decrease in the degree of acetylation (14-19%) in LMWC compared to native chitosan ( approximately 26%). Minimum inhibitory concentration of LMWC towards 10(6) CFU ml(-1) of B. cereus was 0.01% (w/v) compared to 0.03% for 10(4) CFU ml(-1) of E. coli. SEM revealed pore formation as well as permeabilization of the bacterial cells, as also evidenced by increased carbohydrate and protein contents as well as the cytoplasmic enzymes in the cell-free supernatants. N-terminal sequence analyses of the released proteins revealed them to be cytoplasmic/membrane proteins. Upon GLC, the supernatant showed characteristic fatty acid profiles in E. coli, thus subscribing to detachment of lipopolysaccharides into the medium, whereas that of B. cereus indicated release of surface lipids. The mechanism for the observed bactericidal activity of LMWC towards both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria has been discussed.