Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 25339754
J. Neurosci. 2014 Oct;34(43):14430-42
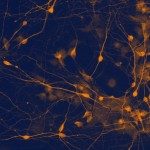
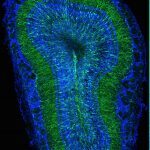
Subventricular zone (SVZ) neurogenesis continuously provides new GABA- and dopamine (DA)-containing interneurons for the olfactory bulb (OB) in most adult mammals. DAergic interneurons are located in the glomerular layer (GL) where they participate in the processing of sensory inputs. To examine whether adult neurogenesis might contribute to regeneration after circuit injury in mice, we induce DAergic neuronal loss by injecting 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) in the dorsal GL or in the right substantia nigra pars compacta. We found that a 6-OHDA treatment of the OB produces olfactory deficits and local inflammation and partially decreases the number of neurons expressing the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) near the injected site. Blockade of inflammation by minocycline treatment immediately after the 6-OHDA administration rescued neither TH(+) interneuron number nor the olfactory deficits, suggesting that the olfactory impairments are most likely linked to TH(+) cell death and not to microglial activation. TH(+) interneuron number was restored 1 month later. This rescue resulted at least in part from enhanced recruitment of immature neurons targeting the lesioned GL area. Seven days after 6-OHDA lesion in the OB, we found that the integration of lentivirus-labeled adult-born neurons was biased: newly formed neurons were preferentially incorporated into glomerular circuits of the lesioned area. Behavioral rehabilitation occurs 2 months after lesion. This study establishes a new model into which loss of DAergic cells could be compensated by recruiting newly formed neurons. We propose that adult neurogenesis not only replenishes the population of DAergic bulbar neurons but that it also restores olfactory sensory processing.