Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 27457935
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2016 08;113(32):9081-6
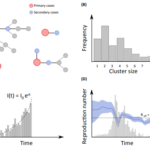
With more than 1,700 laboratory-confirmed infections, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) remains a significant threat for public health. However, the lack of detailed data on modes of transmission from the animal reservoir and between humans means that the drivers of MERS-CoV epidemics remain poorly characterized. Here, we develop a statistical framework to provide a comprehensive analysis of the transmission patterns underlying the 681 MERS-CoV cases detected in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) between January 2013 and July 2014. We assess how infections from the animal reservoir, the different levels of mixing, and heterogeneities in transmission have contributed to the buildup of MERS-CoV epidemics in KSA. We estimate that 12% [95% credible interval (CI): 9%, 15%] of cases were infected from the reservoir, the rest via human-to-human transmission in clusters (60%; CI: 57%, 63%), within (23%; CI: 20%, 27%), or between (5%; CI: 2%, 8%) regions. The reproduction number at the start of a cluster was 0.45 (CI: 0.33, 0.58) on average, but with large SD (0.53; CI: 0.35, 0.78). It was >1 in 12% (CI: 6%, 18%) of clusters but fell by approximately one-half (47% CI: 34%, 63%) its original value after 10 cases on average. The ongoing exposure of humans to MERS-CoV from the reservoir is of major concern, given the continued risk of substantial outbreaks in health care systems. The approach we present allows the study of infectious disease transmission when data linking cases to each other remain limited and uncertain.