Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 23986799
Commun Integr Biol 2013 Jul;6(4):e24243
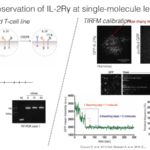
Class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) is a lipid kinase playing key roles in many signaling pathways regulating cell survival and growth. Besides its important role in signal transduction, PI3K is also involved in actin and membrane reorganization such as protrusion, adhesion, phagocytosis and macropinocytosis. Receptor-mediated endocytosis is initiated by plasma membrane reorganization creating buds that then mature to small vesicles. Whereas most of endocytic mechanisms involve actin polymerization, PI3K requirement has not been clearly investigated. Our study identifies class I PI3K as a key player in clathrin-independent endocytosis of the interleukin 2 receptor (IL-2R) in contrast to the clathrin-dependent entry of transferrin (Tf). IL-2R is a cytokine receptor, inducing several signaling cascades such as PI3K, that are essential for the immune response. We have shown previously that IL-2R can be internalized with or without IL-2 and this process requires dynamin, actin and their regulators cortactin, N-WASP, Rac1 and the kinases Pak. Our recent work reveals that PI3K regulates Rac1 during IL-2R uptake in two ways: via its catalytic activity (p110) and via its regulatory factor (p85). Indeed, the catalytic activity of PI3K is required for both constitutive and IL-2 induced uptake of cytokine receptors, in lymphocytes as well as in epithelial cells. Interestingly, Vav2, a Rac1 GTPase exchange factor (GEF) induced upon PI3K activation, is specifically involved and recruited during IL-2R uptake. The second action of PI3K is via its regulatory subunit, p85, which binds activated Rac1 and IL-2R; this interaction being enhanced upon IL-2 treatment. Thus, PI3K regulates both the activation of Rac1 and its recruitment during IL-2R endocytosis. Finally, our results identify a link between cytokine receptors signaling and clathrin-independent endocytosis.