Lien vers Pubmed [PMID] – 23157006
Nat Prod Commun 2012 Oct;7(10):1347-50
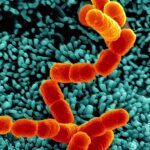
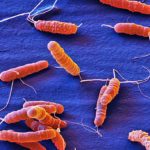
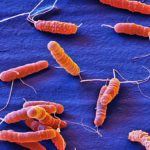
In this study we investigated the anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of four isopentenyloxycinnamyl derivatives from the Australian shrub Boronia pinnata Sm. (Rutaceae), structurally related to boropinic acid: (E)-3-(4-(3-methylbut-2-enyloxy)-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acrylaldehyde (1), boropinol C (2), boropinal (3) and boropinol A (4). In vitro growth of H. pylori strains 26695 and B128 was analyzed in liquid culture with increasing doses of these compounds. Bacterial morphology was visualized by scanning electron microscopy. The in vivo effects of the two most efficient molecules that reduced bacterial growth in vitro, compounds 3 and 4, were investigated on H. pylori gastric colonization in the mouse model. The presence of these compounds in the bacterial cultures led to alterations of bacterial surface and flagella. In vivo, both compounds 3 and 4 at 250 microM reduced significantly the ability of H pylori to colonize the gastric mucosa of mice, compared with untreated ones. These data indicate that these natural isopentenyloxycinnamyl derivatives related to boropinic acid can be considered as novel antibacterial agents with anti-H. pylori activity.