Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 25002399
J. Cell. Sci. 2014 Sep;127(Pt 17):3840-51
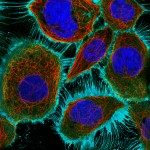
The midbody remnant (MBR) that is generated after cytokinetic abscission has recently attracted a lot of attention, because it might have crucial consequences for cell differentiation and tumorigenesis in mammalian cells. In these cells, it has been reported that the MBR is either released into the extracellular medium or retracted into one of the two daughter cells where it can be degraded by autophagy. Here, we describe a major alternative pathway in a variety of human and mouse immortalized cells, cancer cells and primary stem cells. Using correlative light and scanning electron microscopy and quantitative assays, we found that sequential abscissions on both sides of the midbody generate free MBRs, which are tightly associated with the cell surface through a Ca(2+)/Mg(2+)-dependent receptor. Surprisingly, MBRs move over the cell surface for several hours, before being eventually engulfed by an actin-dependent phagocytosis-like mechanism. Mathematical modeling combined with experimentation further demonstrates that lysosomal activities fully account for the clearance of MBRs after engulfment. This study changes our understanding of how MBRs are inherited and degraded in mammalian cells and suggests a mechanism by which MBRs might signal over long distances between cells.