Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 20023636
Nat. Med. 2010 Jan;16(1):83-9
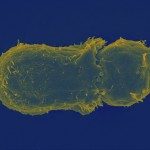
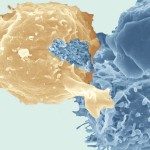
Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is a lymphotropic retrovirus whose cell-to-cell transmission requires cell contacts. HTLV-1-infected T lymphocytes form ‘virological synapses’, but the mechanism of HTLV-1 transmission remains poorly understood. We show here that HTLV-1-infected T lymphocytes transiently store viral particles as carbohydrate-rich extracellular assemblies that are held together and attached to the cell surface by virally-induced extracellular matrix components, including collagen and agrin, and cellular linker proteins, such as tetherin and galectin-3. Extracellular viral assemblies rapidly adhere to other cells upon cell contact, allowing virus spread and infection of target cells. Their removal strongly reduces the ability of HTLV-1-producing cells to infect target cells. Our findings unveil a novel virus transmission mechanism based on the generation of extracellular viral particle assemblies whose structure, composition and function resemble those of bacterial biofilms. HTLV-1 biofilm-like structures represent a major route for virus transmission from cell to cell.