Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 6328660
Science 1984 Jul;225(4657):59-63
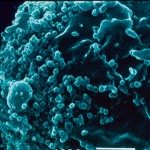
Lymphadenopathy associated virus ( LAV ) has been isolated from patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or lymphadenopathy syndrome. Since the immune deficiency in AIDS seems to be primarily related to the defect of the helper-inducer T lymphocyte subset, the possibility that LAV is selectively tropic for this subset was investigated. Fractionation of T lymphocytes was achieved by cellular affinity chromatography with monoclonal antibodies. In a hemophilic patient who was a healthy carrier of LAV , reverse transcriptase activity and virus particles detected by electron microscopy were found only in cultures of helper-inducer lymphocytes. When infected with LAV in vitro, lymphocyte subsets from normal individuals yielded similar results. Virus production was associated with impaired proliferation, modulation of T3-T4 cell markers, and the appearance of cytopathic effects. The results provide evidence for the involvement of LAV in AIDS.