Link to Pubmed [PMID] – 33055216
Link to DOI – 10.1073/pnas.2005389117
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020 10; 117(43): 26784-26794
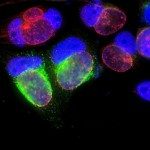
The obligate intracellular bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis, the causative agent of trachoma and sexually transmitted diseases, multiply in a vacuolar compartment, the inclusion. From this niche, they secrete “effector” proteins, that modify cellular activities to enable bacterial survival and proliferation. Here, we show that the host autophagy-related protein 16-1 (ATG16L1) restricts inclusion growth and that this effect is counteracted by the secretion of the bacterial effector CT622/TaiP (translocated ATG16L1 interacting protein). ATG16L1 is mostly known for its role in the lipidation of the human homologs of ATG8 (i.e., LC3 and homologs) on double membranes during autophagy as well as on single membranes during LC3-associated phagocytosis and other LC3-lipidation events. Unexpectedly, the LC3-lipidation-related functions of ATG16L1 are not required for restricting inclusion development. We show that the carboxyl-terminal domain of TaiP exposes a mimic of an eukaryotic ATG16L1-binding motif that binds to ATG16L1’s WD40 domain. By doing so, TaiP prevents ATG16L1 interaction with the integral membrane protein TMEM59 and allows the rerouting of Rab6-positive compartments toward the inclusion. The discovery that one bacterial effector evolved to target ATG16L1’s engagement in intracellular traffic rather than in LC3 lipidation brings this “secondary” activity of ATG16L1 in full light and emphasizes its importance for maintaining host cell homeostasis.